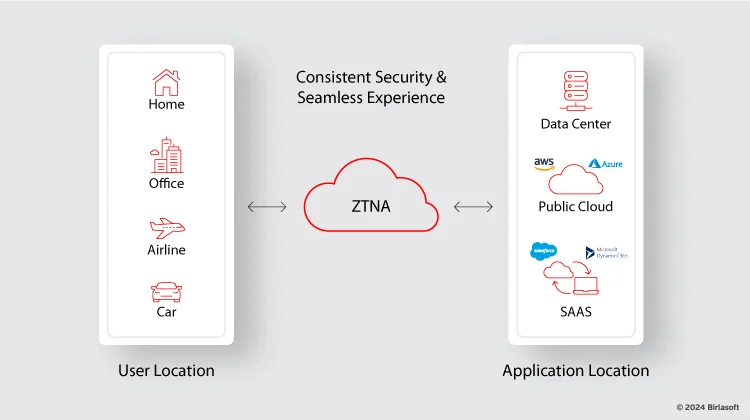
The key components of ZTNA include –
- Never Trust, Always Verify – ZTNA operates with the principle that each access request must be verified and authenticated.
- Least Privilege Access – Grant minimum level of access necessary for users to perform their tasks.
- Continuous Monitoring and Analytics – Real-time monitoring of network traffic, user, and device behavior to detect any potential threats or anomalies.
- Contextual Access Controls: Access decisions are based on contextual factors such as user identity, location, time of access, device health, and behavior.
- Micro-Segmentation: Network is divided into smaller segments and access controls are applied specific to each segment.
- Dynamic Policy Enforcement: Adjusts security policies dynamically based on changes in user behavior, network conditions or threat intelligence.
ZTNA strategies are undergoing constant evolution to ensure a holistic approach to security that addresses the changing landscape of threats and technological advancements. Some of these are – Integration of AI and ML into ZTNA, Integration of ZTNA and IAM and Integration of Zero Trust into DevSecOps.
As per Gartner, atleast 70% of new remote access deployments will be served mainly by ZTNA instead of VPN services by 2025 – up from less than 10% at the end of 2021.