What is Hybrid Cloud?
Hybrid Cloud Explained
A hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud services and allows IT to manage workloads by moving them across cloud solutions to optimize costs and efficiency. It brings the best of both worlds by tapping into the benefits of public and private cloud solutions while avoiding their downsides.
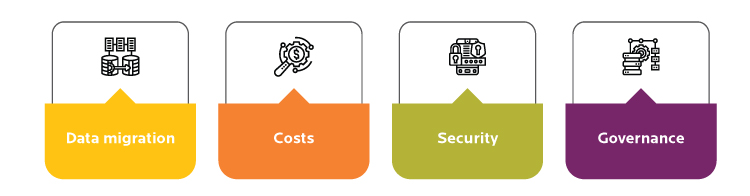
For instance, enterprises embrace the public cloud for its scalability, flexibility, and low costs. However, they still express concerns over security and privacy. They can't control the architecture of a public cloud, which prompts a more expensive, less flexible private cloud. Instead, enterprises could leverage both models by:
- Storing sensitive information on a private cloud or an on-premise data center
- Use the highly scalable public cloud for less-sensitive data or applications
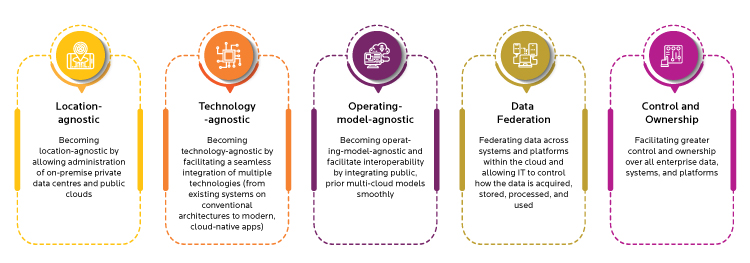
For hybrid cloud models to bear fruit, enterprises must expand their horizons and think beyond the typical public-private cloud model. They should envision an architecture that also manages on-premise data, colocation, hosting services and facilitates interoperability between different cloud environments. Being truly hybrid means:
- Becoming location-agnostic by allowing administration of on-premise private data centers and public clouds
- Becoming technology-agnostic by facilitating a seamless integration of multiple technologies (from existing systems on conventional architectures to modern, cloud-native apps)
- Becoming operating-model-agnostic and facilitate interoperability by integrating public, private, or multi-cloud models smoothly
- Federating data across systems and platforms within the cloud and allowing IT to control how the data is acquired, stored, processed, and used
- Facilitating greater control and ownership over all enterprise data, systems, and platforms
Hybrid Cloud Explained
Trends in Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud Adoption
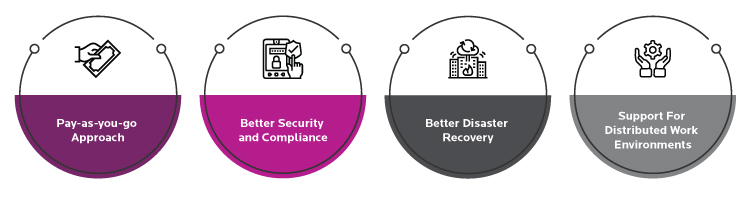
As distributed work environments increasingly become mainstream, hybrid is destined to become the go-to IT infrastructure model to thrive. Enterprises appreciate the vast benefits of such an approach in optimizing costs, performance, and security while simplifying regulatory compliance across geographies. Besides, in the age of hyper-connectivity with the rise of edge computing and IoT, there’s a growing need for enterprise infrastructure to be more elastic, agile, and modernize their apps on the cloud.
Hybrid Cloud Adoption Statistics
According to the 2021 State of the Cloud report by Flexera, 82% of the enterprises surveyed already had a hybrid cloud strategy. Another survey predicts that 80% of organizations will migrate to the cloud, hosting, or colocation services by 2025. These numbers are projected to grow as more enterprises increase their annual cloud spending - for 36%, this already exceeded $12 million.
Hybrid Cloud Data Management
A successful cloud adoption strategy must navigate significant challenges that revolve around mindset, technologies, cybersecurity, and changing business requirements. There's an additional challenge for a hybrid cloud adoption strategy - data management across multiple locations and environments.
Enterprise data is scattered across cloud and on-premise environments - gathered from various sources and stored in different formats. Accessing the correct data and using it to drive decision-making is a monumental challenge that enterprises face. As a result, they’re constantly seeking ways to optimize their data assets and set up a unified platform that provides centralized access to all organizational data, regardless of the source, format, or location.
With an increase in the adoption of hybrid cloud models, enterprises must transform their data management strategy and embrace hybrid cloud data management. This should be a part of an enterprise’s digital transformation roadmap. Before exploring the nitty-gritty of such an approach, let’s understand the concept.